SMART-G, a Monte Carlo GPU Radiative Transfer code
- Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Monte Carlo Radiative Transfer solver
- GPU accelerated using the CUDA framework (massively parallel processing)
- Coded in Python and PyCUDA
- Physical processes
- scattering (molecules, water, aerosols, clouds)
- absorption (molecules, water, aerosols) and with extended band models (K distribution, …)
- reflection/refraction (Fresnel, atmospheric refraction)
- polarization
- Plane-parallel or spherical-shell atmosphere
- Surface
- wind roughened sea surface
- bidirectional reflectance distribution function
- horizontal variation of surface albedo
- Fast spectral computation
- 3-Dimensional characteristics
- 3D optical properties of atmosphere
- 3D objects
Applications
Simulation of radiance in limb geometry with atmospheric refraction
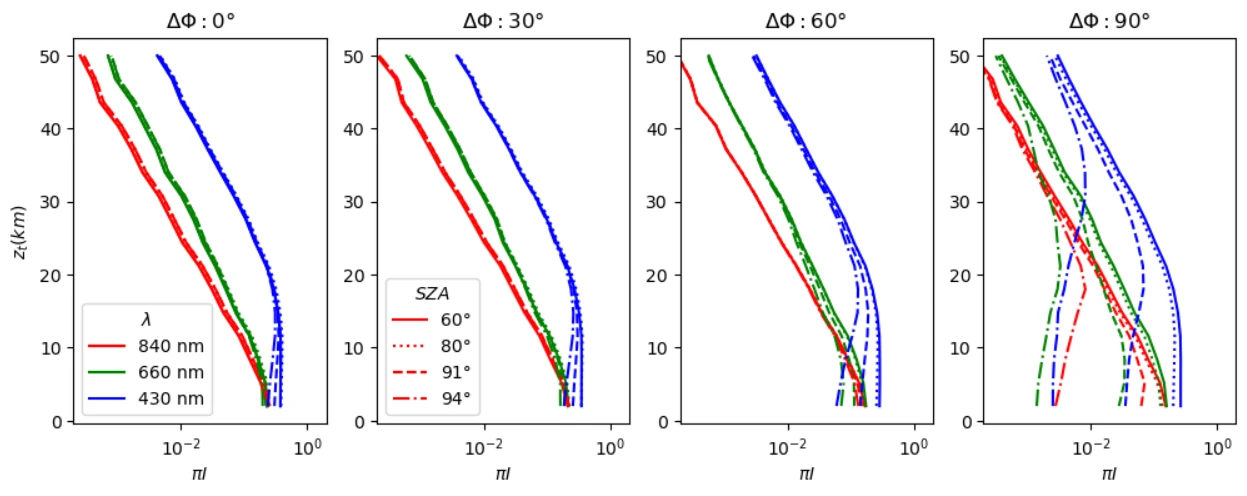
Limb diffuse radiance for an observer at 120km altitude as a function of the tangent height for different relative azimuths to the Sun (ΔΦ = 0, 30, 60, 90°), 3 wavelengths (430, 660 and 840 nm) and 4 solar zenith angles (SZA = 60, 80, 91 and 94°).
The computation time with 105 photons/height/azimuth is about 1s with a GeForce RTX3090 graphics card.
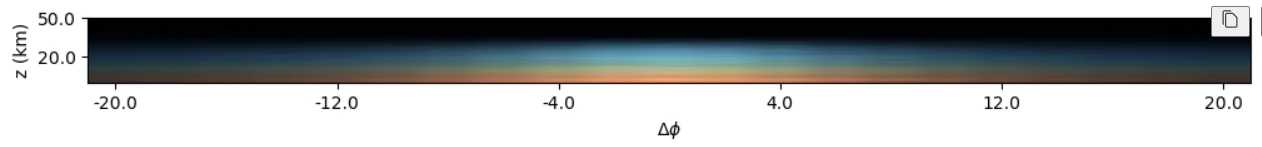
RGB composite (430nm, 660nm, 840nm) of the limb radiance for a low Sun (SZA=94°) in the forward directions up to ΔΦ = 20°.
Simulation of topographic and 3D objects influence on radiance
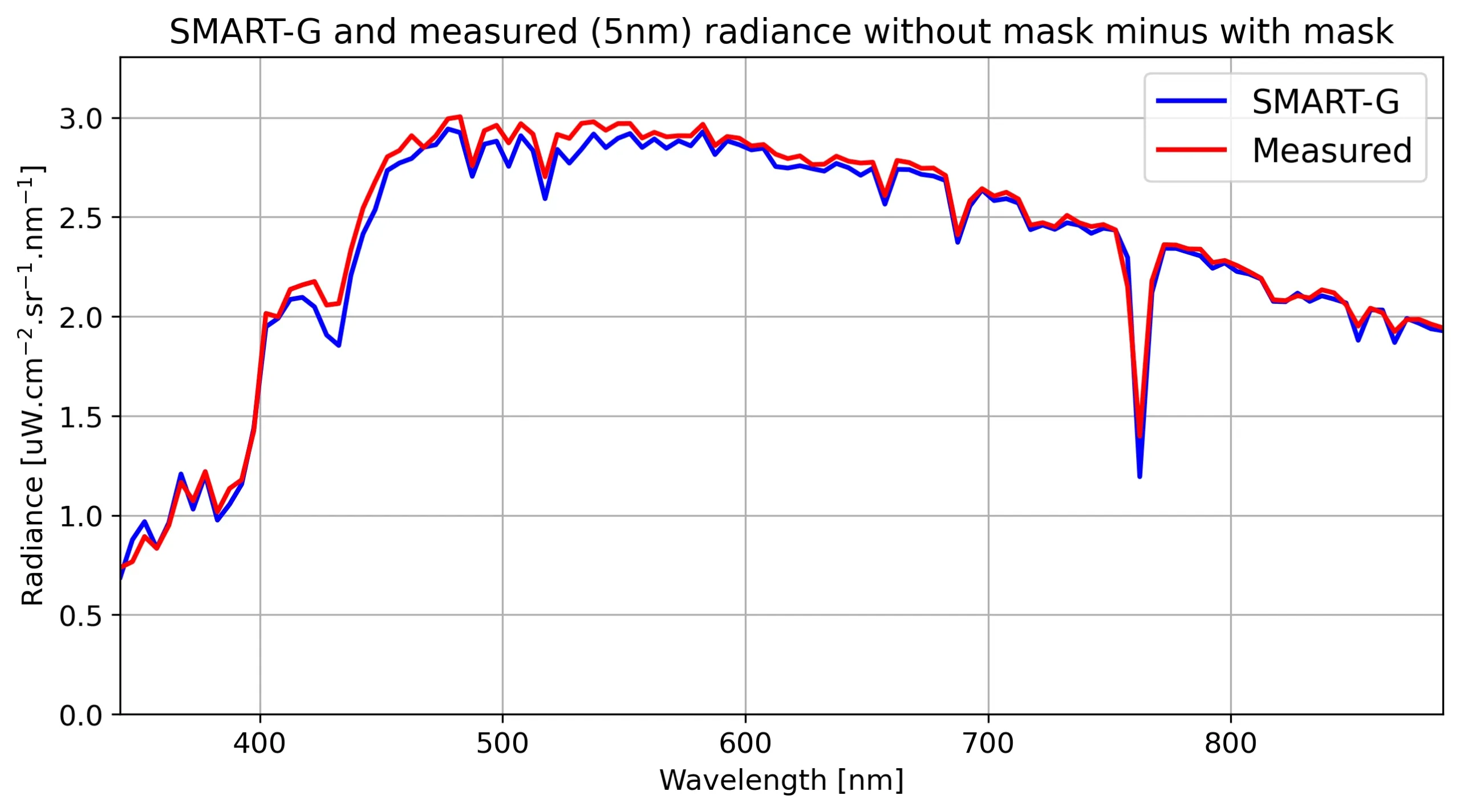
Radiometric calibration of in situ spectro-radiometer at the top of a mountain. The radiometer is viewing a horizontal plate of known bidirectional reflectance with the Sun disk unobscured and masked, allowing a determination of the direct component of downwelling planar irradiance.
The SMART-G simulation is done with a proper k-distribution at the same spectral resolution as the instrument.
Simulation of 2D adjacency effects
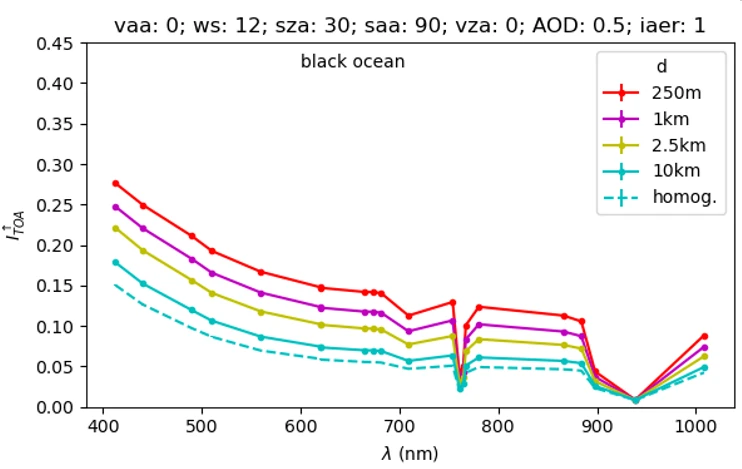
Simulation of TOA spectra of the Sentinel-3/OLCI sensor for a black ocean pixel as a function of the distance d to the linear coastline separating ocean and land covered by snow and ice. The principal plane is parallel to the coastline.
Simulation of 3D clouds
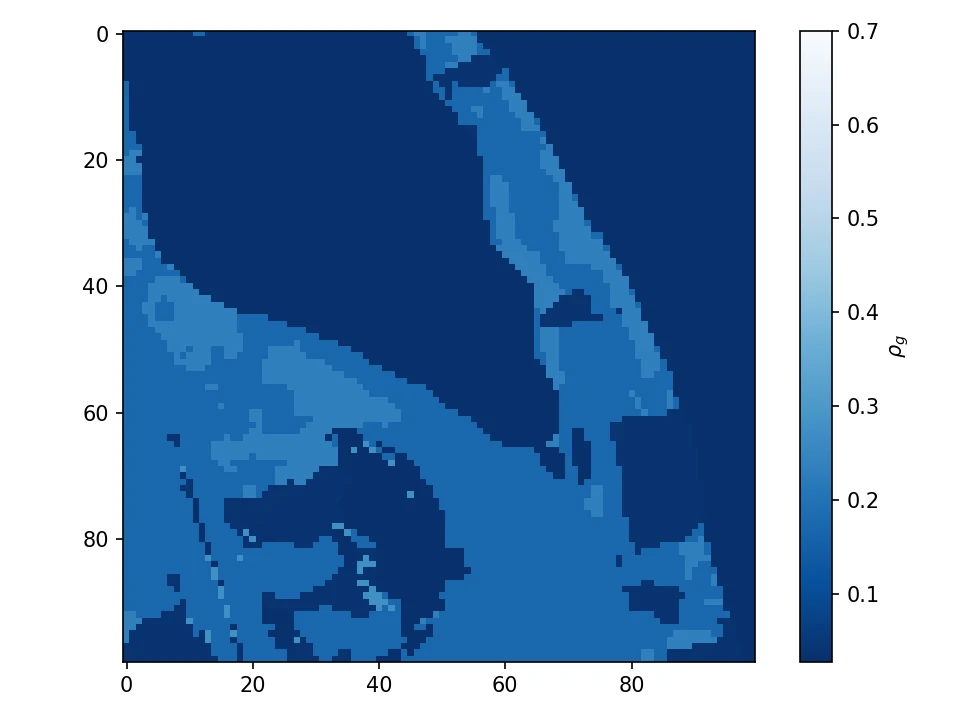
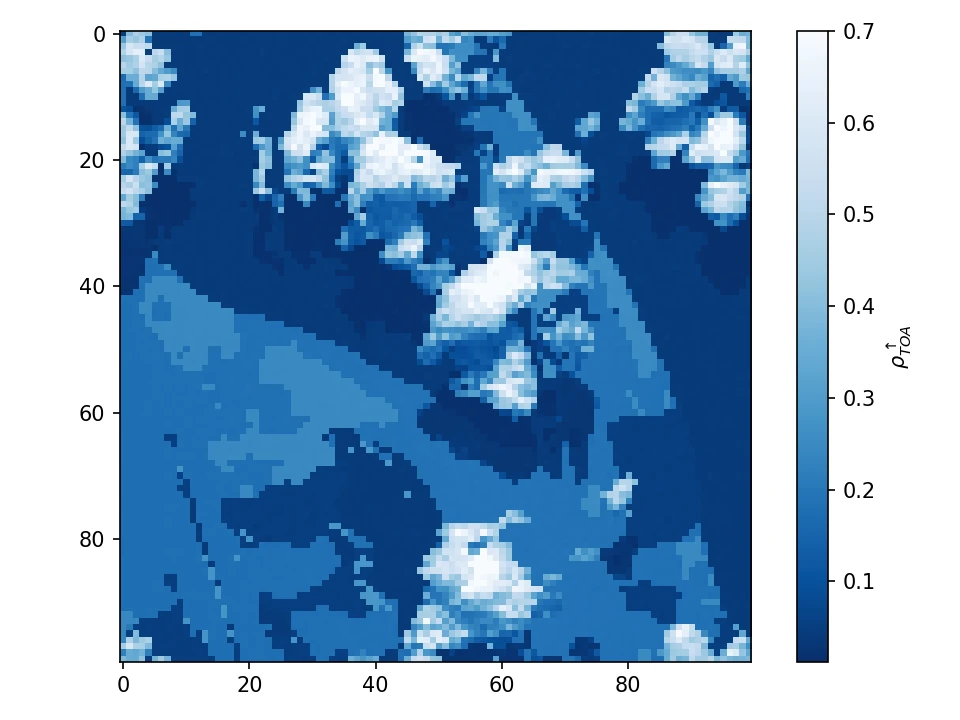
Maps of surface (left) and TOA (right) reflectances at 710 nm for a cloudy scene, simulated using Large Eddy Simulation microphysical outputs and for a continental aerosol polluted atmosphere. The horizontal resolution is 66 m and there are 53 vertical layers for a total of atmospheric cell of 100x100x53. The surface is a lambertian reflector whose spectral albedo is obtained from Sentinel-2 Land Cover map.